This article not only explores the key differences between stress and burnout but also helps readers recognize their symptoms while understanding their impact on mental and physical health. Moreover, it provides practical recovery strategies, including effective stress management techniques, proven burnout prevention methods, and essential lifestyle changes for long-term well-being. Additionally, with expert insights and highly actionable advice, this comprehensive guide empowers individuals to regain balance, enhance resilience, and, most importantly, seek professional help whenever needed.

Understanding the Differences Between Burnout and Stress
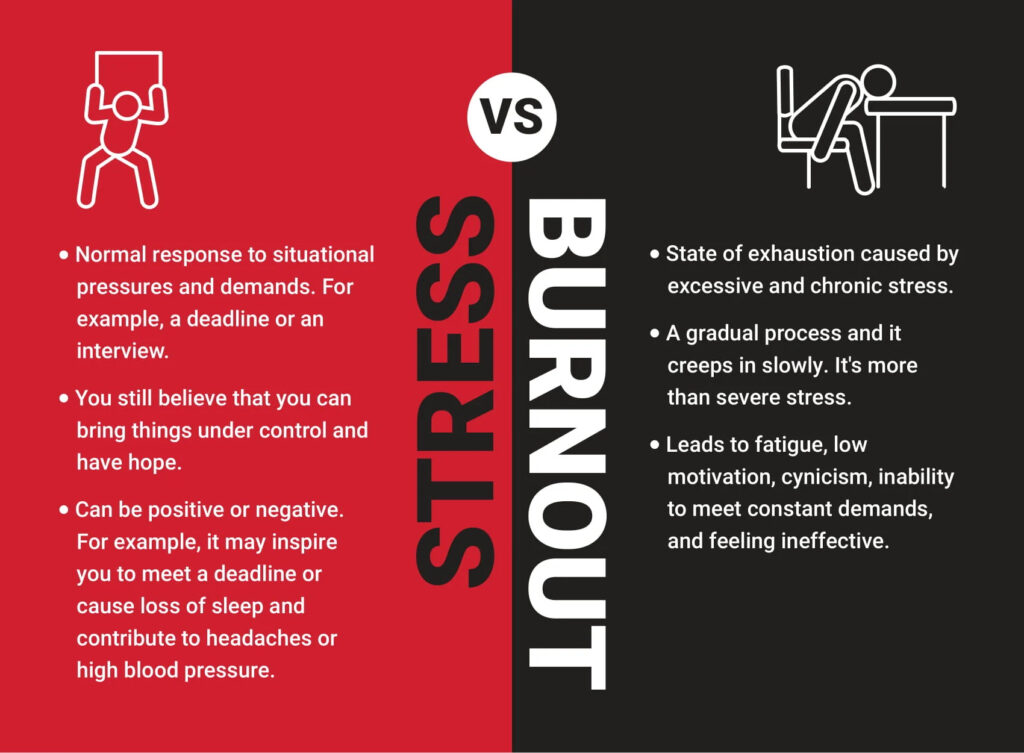
Defining Stress
Stress is the body’s natural response to challenges. It can be short-term or long-term, and it often arises from daily responsibilities, work pressure, or personal issues. While mild stress can enhance focus and performance, chronic stress, on the other hand, negatively affects mental and physical health. Therefore, recognizing stress early is essential for maintaining overall well-being. Moreover, managing it properly can prevent further complications.
What Is Burnout?
Burnout is a state of emotional, physical, and mental exhaustion caused by prolonged stress. As a result, it leads to a lack of motivation, feelings of helplessness, and reduced effectiveness in daily tasks. Unlike stress, which may involve temporary overwhelm, burnout feels like a complete shutdown, making it difficult to recover without intervention. Consequently, understanding the early warning signs is crucial for prevention. In addition, knowing the difference between burnout and stress allows for appropriate intervention strategies.
Recognizing the Symptoms
Signs of Stress
Stress manifests in different ways, and it is important to recognize its signs early. These include:
- Increased heart rate, which can be alarming
- Muscle tension, making it harder to relax
- Irritability, often leading to conflicts
- Anxiety, which can disrupt focus
- Difficulty sleeping, resulting in fatigue
- Trouble concentrating, which affects productivity
Since stress can impact multiple aspects of life, taking timely action can prevent its escalation. Moreover, early intervention can reduce its long-term effects.
Symptoms of Burnout
Burnout symptoms, on the other hand, develop gradually and often include:
- Chronic fatigue, making even small tasks overwhelming
- Detachment from work or personal life, leading to emotional numbness
- Loss of interest in activities, reducing engagement
- Feeling ineffective or unaccomplished, despite effort
- Frequent headaches or digestive issues, impacting overall health
Notably, burnout does not disappear on its own. Therefore, addressing it with proactive strategies is necessary. Additionally, seeking professional support can accelerate recovery.
Causes and Risk Factors
Common Causes of Stress
Stress can arise from various sources, and understanding them is crucial for effective management. Some of the most common causes include:
- Work deadlines, which create pressure
- Financial struggles, leading to worry and anxiety
- Relationship conflicts, often causing emotional distress
- Health concerns, which add to uncertainty
- Overcommitment, making time management difficult
Since these factors vary for each person, finding tailored coping strategies can be beneficial. Furthermore, addressing the root causes can help in long-term stress management.
Factors Leading to Burnout
Burnout, in contrast, often results from prolonged exposure to high-pressure environments. Some of the most frequent causes include:
- Excessive workload, which reduces work-life balance
- Lack of control over tasks, leading to frustration
- Poor work-life balance, increasing emotional exhaustion
- Insufficient social support, making challenges harder to manage
- Unclear job expectations, which create uncertainty
Recognizing these risk factors allows individuals to take preventive measures early. Moreover, making small adjustments in work and personal life can significantly reduce the risk of burnout.
The Impact on Mental and Physical Health
Effects of Stress on the Body
Chronic stress affects multiple systems in the body, and over time, it can lead to severe health complications. Some of the most notable effects include:
- High blood pressure, increasing the risk of heart disease
- Suppressed immune function, making illness more frequent
- Digestive issues, which cause discomfort
- Increased risk of heart disease, further impacting well-being
- Mental health disorders like anxiety and depression, worsening emotional stability
Although stress is a natural response, prolonged exposure can be damaging. Therefore, managing stress effectively is necessary for maintaining overall health.
How Burnout Affects Overall Well-being
Burnout, similarly, impacts emotional stability, relationships, and work performance. It increases the risk of:
- Persistent fatigue, making daily tasks difficult
- Emotional detachment, affecting relationships and social interactions
- Reduced cognitive function, lowering problem-solving skills
- Substance abuse, as a coping mechanism
- Insomnia, worsening physical and mental health
Because burnout affects both personal and professional life, addressing it as soon as possible is essential. Moreover, prioritizing self-care can significantly improve recovery.
Recovery Strategies
Managing Stress Effectively
Reducing stress requires proactive strategies, and incorporating them into daily life can make a significant difference. Some effective methods include:
- Practicing mindfulness and meditation, which promote relaxation
- Prioritizing tasks with time management, reducing overwhelm
- Engaging in physical activities, improving mood and energy levels
- Seeking social support, which enhances emotional resilience
- Getting quality sleep, essential for recovery
By integrating these habits consistently, individuals can mitigate the negative effects of stress. Additionally, maintaining a balanced lifestyle can prevent stress from recurring frequently.
Overcoming Burnout
Recovering from burnout demands deeper intervention, as it affects multiple aspects of life. Essential steps include:
- Setting boundaries to limit workload, preventing further exhaustion
- Taking regular breaks, allowing for mental recovery
- Finding purpose in work, increasing motivation
- Seeking professional guidance, which provides structured support
- Cultivating a supportive environment, fostering well-being
Since burnout takes time to heal, patience and persistence are necessary throughout the recovery process. Furthermore, implementing self-care routines can promote long-term healing.
Lifestyle Changes for Long-Term Well-being
Building Resilience
Developing resilience helps manage stress and prevent burnout. Fortunately, effective techniques include:
- Developing a positive mindset, shifting perspectives
- Practicing gratitude, enhancing emotional strength
- Learning stress-reduction techniques, creating better coping mechanisms
- Improving emotional intelligence, leading to better self-awareness
When resilience becomes a habit, handling challenges becomes easier. Additionally, strengthening emotional well-being contributes to personal growth.
Creating Work-Life Balance
A balanced lifestyle reduces stress and prevents burnout. In particular, focusing on key aspects can make a big difference:
- Establishing clear work boundaries, ensuring personal time
- Engaging in hobbies, which boost creativity and relaxation
- Spending quality time with loved ones, strengthening relationships
- Taking vacations without guilt, allowing for true rejuvenation
A well-balanced life not only improves productivity but also enhances overall happiness. Moreover, prioritizing leisure activities contributes to long-term well-being.
Seeking Professional Help
When to Consult a Specialist
If stress or burnout interferes with daily life, professional intervention may be necessary. Some key indicators include:
- Persistent anxiety or depression, affecting daily functioning
- Loss of motivation, making tasks feel overwhelming
- Physical symptoms like headaches or insomnia, signaling deeper issues
- Difficulty managing emotions, leading to frequent distress
Recognizing these warning signs early can lead to faster recovery. Moreover, therapy and professional guidance can provide structured coping mechanisms.
Available Treatment Options
Support from mental health professionals can make a significant difference. Fortunately, various treatment options are available, such as:
- Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT), which improves thought patterns
- Medication for anxiety or depression, assisting in symptom management
- Stress management coaching, providing personalized guidance
- Support groups, offering shared experiences and encouragement
By exploring these options, individuals can find a path to healing that works best for them. Additionally, combining different strategies may enhance recovery effectiveness.
Almost everything will work again if you unplug it for a few minutes, including you.
Anne Lamott
Conclusion
Recognizing the difference between stress and burnout is crucial for effective recovery. While stress can often be managed with lifestyle adjustments, burnout requires deeper intervention. However, by prioritizing self-care, setting boundaries, and seeking support when needed, individuals can restore their well-being and maintain long-term health. Furthermore, making consistent efforts to improve mental and physical health ensures lasting resilience.

